Obesity and Metabolic Surgery
SADI-S
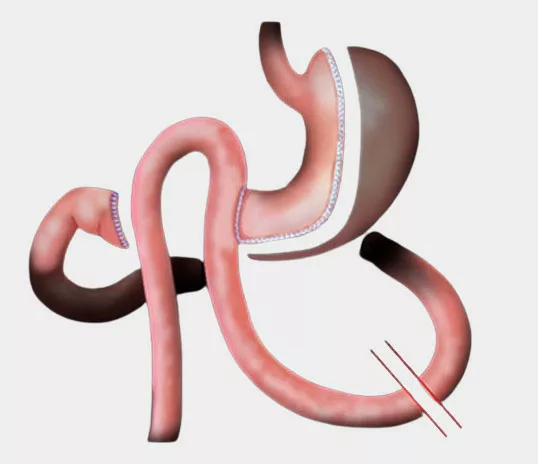
Definition & principle
SADI-S (single anastomosis duodeno-ileal bypass with sleeve gastrectomy) is a procedure combining sleeve gastrectomy with bowel bypass. It is a recent technique that is being developed and integrated into the arsenal of obesity surgery procedures.
This technique is restrictive, with much malabsorption. It is derived from the biliopancreatic bypass (BPD), reducing the number of anastomoses. It limits the quantity of food ingested and its assimilation by the intestine.
It is considered as effective as BPD but with fewer complications. It remains reserved for very severe cases of obesity with significant metabolic repercussions.
It combines a sleeve gastrectomy with a short circuit of the small intestine. Food is only digested by the digestive juices and assimilated over a 2 to 3m portion of the small intestine.
Features
This technique is reserved for very obese patients with a BMI > 60 kg/m2. It is performed by specialized teams.
How does the Operation takes place?
The operation is performed by laparoscopy (5 to 6 small skin incisions are necessary).
The operation lasts between 2 and 3 hours.
The duration of hospitalization is about a week.
Advantages
The weight loss is significant and long-lasting, it is about 90%. The quality of life is average due to the partial digestion of food. The patient must be strictly monitored because of the high risk of deficiencies. Significant supplementation is necessary for life.
This intervention is exceptional.
Expected Weight Loss
The weight loss is significant and long-lasting, it is about 90%. There is little perspective at the moment because this intervention is recent.
Vitamin & Nutritional Deficiencies
Significant deficiencies in vitamin B12, vitamin D and iron; supplements are mandatory.
Deficiencies in vitamins B1, B6, C.
Usual nutritional deficiencies in protein to be supplemented.
Vitamin supplementation is nowadays recommended for life.
we help you achieve your weight-Loss Goals
The surgical management of obesity is based on 4 axes.
The surgical intervention, the preoperative and postoperative nutritional care, a preoperative and sometimes postoperative psychological assessment and follow-up, and a regular and sustained physical activity…