Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Unit
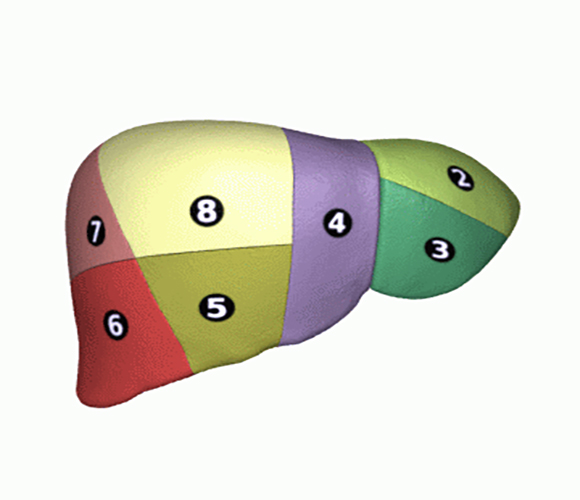
Hepatectomy (right or left)
The principle of a hepatectomy consists of removing part of the liver, removing malignant or benign lesions of the liver. The lesions can be primary (directly from the liver) or secondary, i.e. metastases.
In the case of a minimally invasive operating method (laparoscopy or robot-assisted), the patient in the operating room is prepared with the installation of trocars which will be used to insert the various tools necessary for the operation.
It is an intervention which resects a small part of the liver by removing in one piece the area which contains the liver cancer with the section of its venous, arterial and biliary pedicles.
Hepatectomy is a technical and delicate surgical procedure.
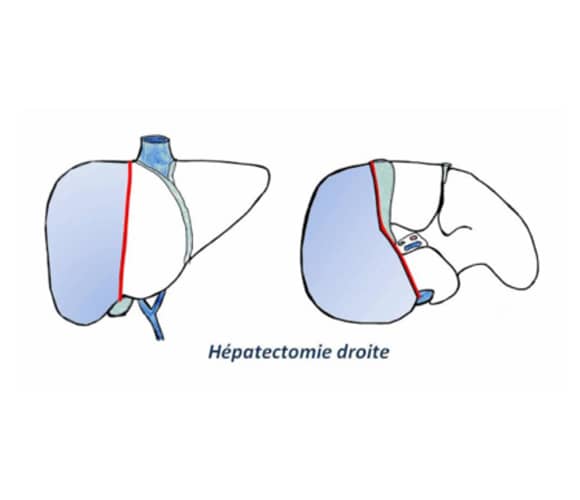
Right hepatectomy:
The operation consists of removing the right part of the liver, that is to say the segments V-VI-VII-VIII of the liver. This is a so-called major hepatectomy.
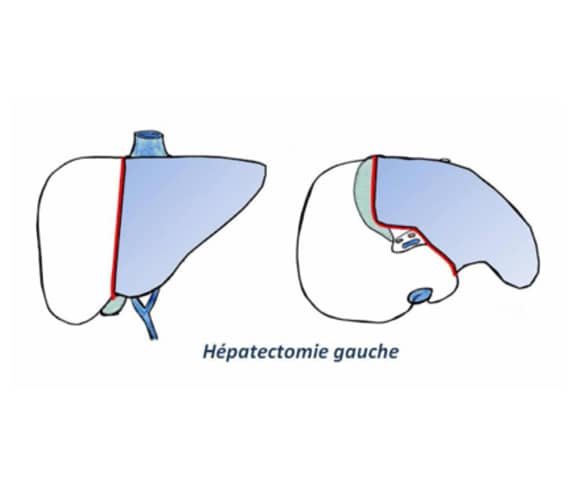
Left hepatectomy:
The operation involves removing the left part of the liver, i.e. segments II-III-IV of the liver. This is a so-called major hepatectomy.
Before the intervention
THE CONSULTATION WITH THE SURGEON
Before a hepatectomy, the patient undergoes various examinations to determine the type of liver injury, and to determine the overall function of the liver and its volume to allow planning of the intervention and its risks.
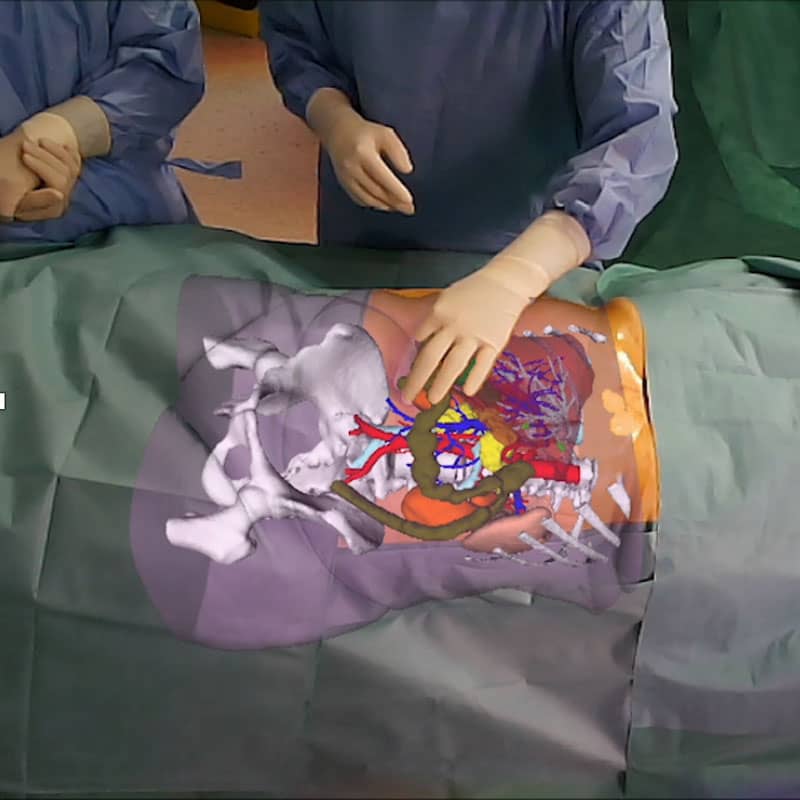
IHU Strasbourg benefits from the latest technological advances in diagnostic imaging tools such as: ultrasound, CT or scanner, MRI, angiography, 3D reconstruction imaging, etc. The result of these images makes it possible to create a three-dimensional model of the patient’s organ, thus obtaining an identical reconstruction which allows personalized solutions to be defined. In special cases, during the operation, the surgeon can use the 3D reconstruction which is accurately superimposed on the patient’s body (augmented reality).
With the results obtained, the surgeon indicates to the patient the objectives of the operation, the technique used and the possible postoperative consequences and complications.
THE CONSULTATION WITH THE ANESTHESIST
Hepatectomy is performed under general anesthesia.
This consultation allows the risks associated with anesthesia to be assessed, taking into account medical, family and surgical history. It is very important to report any health problems (allergies, respiratory and heart problems, medication treatment, alcohol and tobacco consumption). In general, it is strongly recommended to stop drinking alcohol and tobacco a few weeks before the procedure.
Features
This procedure requires the removal in one piece of the area that contains the liver tumors.
The section can be performed with clamping of the hepatic pedicle to reduce bleeding.
Procedure
Hepatectomy can be performed by different surgical techniques such as laparotomy, laparoscopy and robotic-assisted surgery.
The operating time is approximately 3 hours.
The length of hospitalization is approximately 5 days.
These durations are based on an approximation, they may be longer depending on the patient’s state of health.
Benefits and advantages
Hepatectomy is the only intervention that can guarantee the patient’s long-term survival in the event of malignant liver lesions. The liver has the ability to regenerate itself, if the liver tissue is healthy, and to reconstitute itself to its entire normal mass. If the hepatectomy is total (total removal of the liver), it will precede a liver transplant.
Risks and complications
useful information
Download guide: Liver cancer treatments
by Institut National du Cancer, e-cancer.fr
Cancer Info Line
Support throughout your care pathway
Quality patient care is an essential objective, and the patient is at the heart of our concerns.


