Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Unit
Cephalic duodenopancreatectomy
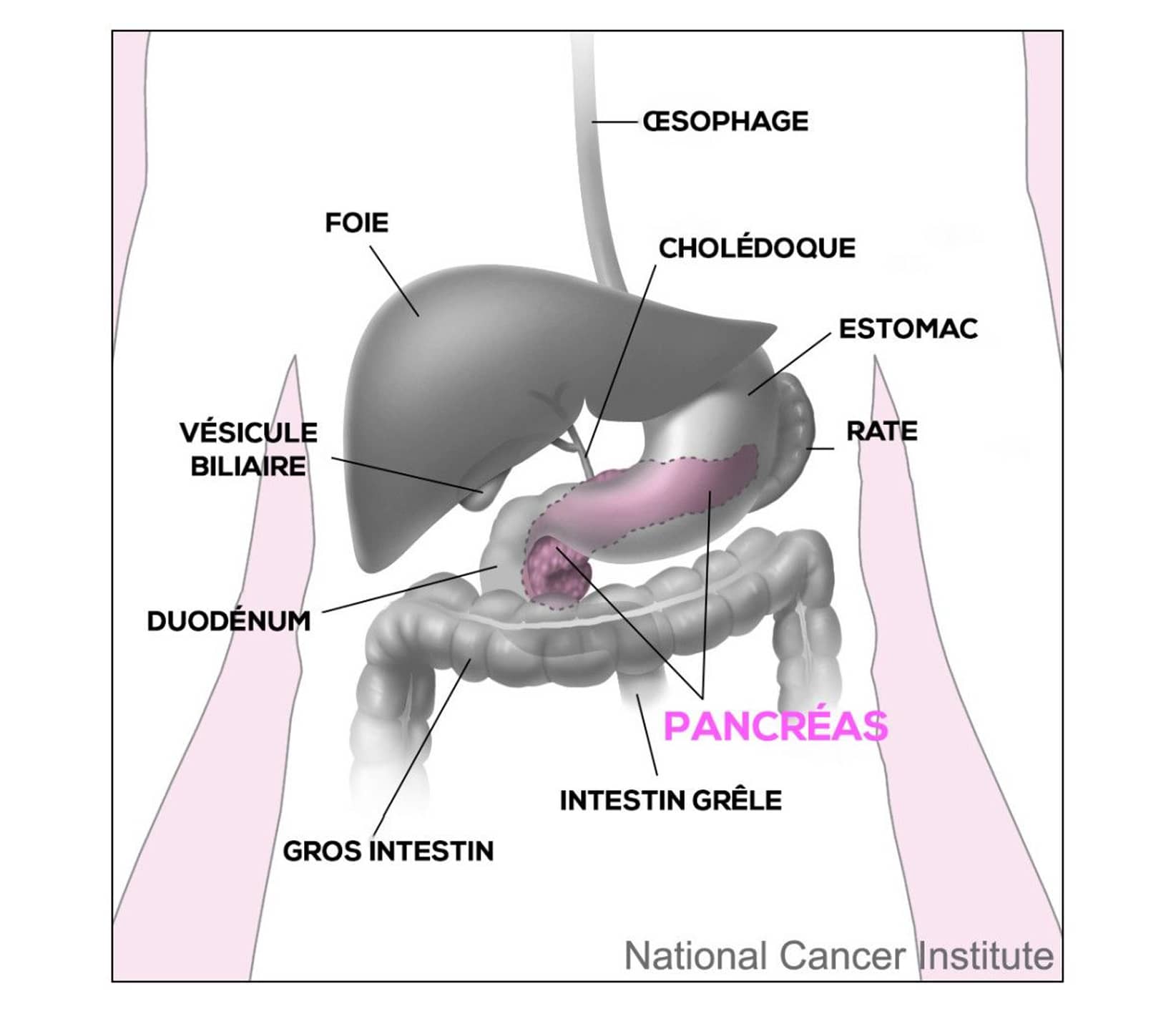
In this procedure, the head of the pancreas (right side) is removed in one piece, along with the entire duodenum and often a small terminal portion of the stomach. The gallbladder is also removed, with the main bile duct passing through the head of the pancreas.
The surgeon then proceeds with digestive reconstruction of the resected organs: liver and pancreas, intestine, stomach, to re-establish the digestive tract circuit.
Before the intervention
THE CONSULTATION WITH THE SURGEON
Before a pancreaticoduodenectomy, the patient undergoes various examinations to determine the type of tumor to allow planning of the intervention and consider its risks.
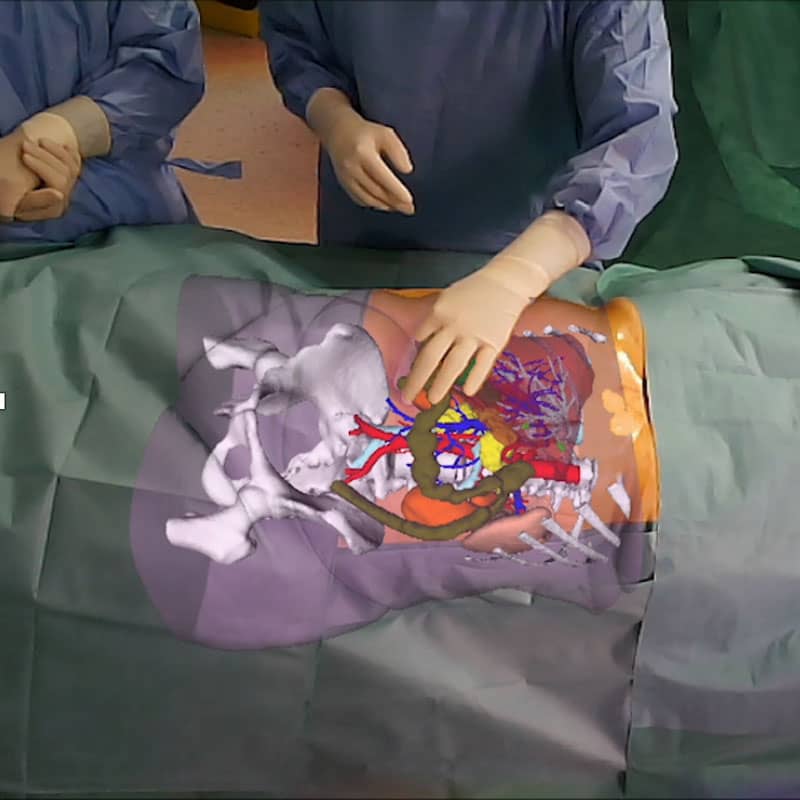
IHU Strasbourg benefits from the latest technological advances in diagnostic imaging tools such as: ultrasound, CT or scanner, MRI, angiography, 3D reconstruction imaging, etc. The result of these images makes it possible to create a three-dimensional model of the patient’s organ, thus obtaining an identical reconstruction which allows personalized solutions to be defined.
With the results obtained, the surgeon indicates to the patient the objectives of the operation, the technique used and the possible postoperative consequences and complications.
THE CONSULTATION WITH THE ANESTHESIST
Duodenopancreatectomy is performed under general anesthesia.
This consultation allows the risks associated with anesthesia to be assessed, taking into account medical, family and surgical history. It is very important to report any health problems (allergies, respiratory and heart problems, medication treatment, alcohol and tobacco consumption). In general, it is strongly recommended to stop drinking alcohol and tobacco a few weeks before the procedure.
Features
Procedure
Cephalic duodenopancreatectomy can be performed as laparotomy, laparoscopy and robotic-assisted surgery, it requires general anesthesia.
The operating time is around 8 hours, and the hospital stay is around 15 days.
Benefits and advantages
This is the only operation that can guarantee long-term survival in cases of malignant tumors of the head of the pancreas or the distal part of the bile duct.
Risks and complications
The main post-operative risks are:
- leakage from the pancreatico-gastric or pancreatico-jejunal anastomosis (pancreatic fistula)
- Post-operative hemorrhage
- In the medium and long term, the onset of diabetes.
Procedure-related mortality is <5%.
useful information
Download guide: Pancreatic cancer treatments
by National Cancer Institute, e-cancer.fr
Cancer Info Line
Support throughout your care pathway
Quality patient care is an essential objective, and the patient is at the heart of our concerns.


